Varicose veins
Blood vessels that enlarge and twist just beneath the surface of your skin are called varicose veins. Your legs, feet, and ankles are the typical locations for these blue or purple bulges. They could itch or hurt.
Smaller red or purple lines that form near to the surface of your skin are called spider veins, which may surround varicose veins. Varicose veins aren’t harmful for the majority of individuals, despite the fact that they can be unattractive and unpleasant. Serious health issues, such as blood clots, can occasionally result from severe varicose veins.
The majority of varicose vein problems may be treated at home by you or by your healthcare practitioner using injections, laser treatment, or surgery.
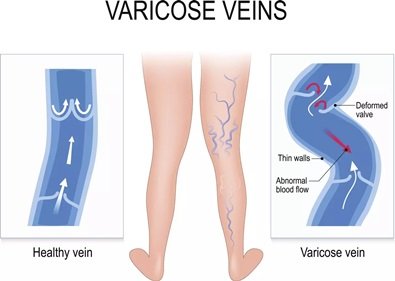

Causes
- Age: Vein walls and valves lose some of their former functionality as we get older.
Veins become stiffer and less flexible. - Gender: The hormones produced by women might cause the vein walls to expand. Due to changes in hormone levels, those who are pregnant, on the birth control pill, or going through menopause are more likely to develop varicose veins.
- Family history: This illness is heritable (runs in families).
- Lifestyle: Prolonged standing or sitting reduces circulation. Blood flow can be reduced by wearing constrictive clothes, such as girdles or jeans with tight waistbands.
- Health in general: Some medical problems, such extreme constipation or specific malignancies, raise the pressure in the veins.
- Use of tobacco products: Varicose veins are more prone to develop in smokers.
- Weight: Carrying too much weight strains blood vessels.
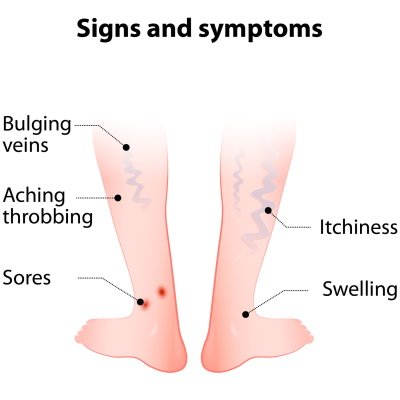
Symptoms
- Veins that are enlarging: Blue or purple veins that are twisted, bulging, and rope-like.
- They occur on your legs, ankles, and feet just below the skin’s surface.
- They may grow in groups.
- Spider veins, tiny red or blue lines, might be seen close by.
- Leg muscles that seem heavy or slow: Especially after exercise, your legs’ muscles may
- feel heavy, exhausted, or sluggish.
- Itching: Varicose veins’ surrounding skin may itch.
- Leg pain: Especially behind the knees, your legs may feel uncomfortable, achy, or sore.
Your muscles might be cramping. - Legs, ankles, and feet can all swell and ache.
- Ulcers and skin discolorations: Varicose veins can result in dark skin discolorations if they are not addressed.
- Venous ulcers (sores) on your skin can result from severe varicose veins.
Site
- Varicose veins typically appear in the lower body, typically on the calves, ankles, and feet.
- Pelvic congestion syndrome is another location where they might manifest, particularly in women who have just given birth.
- Infertility may result from varicocele, or enlarged testicles.

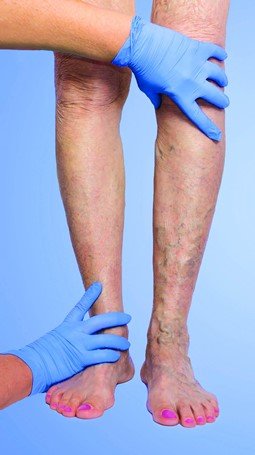
Diagnosis
Your skin’s surface is where varicose veins are located, and they are visible. During a physical examination, medical professionals can make a diagnosis of the illness. While you are seated or standing, they will check and feel your veins.
Your doctor could suggest doing an ultrasound to get clear pictures of your veins and look for any issues. Sound waves are used in this risk-free, painless examination to create images of the tissues inside your body. Blood clots and the functionality of your valves can both be seen on ultrasounds. Carrying too much weight strains blood vessels.
Treatment
- Elevation: Throughout the day, elevate your legs above your waist several times to improve blood flow and lower vein pressure. Supportive socks or stockings with elastic bands might help relieve pain by compressing your veins. Your veins can’t expand because of the compression, which also promotes blood flow. Sclerotherapy is an injection therapy that involves having a medical professional inject a fluid into a vein. The vein walls adhere to one another as a result of the solution. Your vein eventually disappears and transforms into scar tissue.
- Laser therapy: To seal off a damaged vein, medical professionals use a catheter (a lengthy, thin tube) and a laser in a minimally invasive treatment called endovenous thermal ablation.
- Vein surgery: The goal of this technique, also known as ligation and stripping, is to stop blood from pooling by tying off the afflicted vein.
To stop varicose veins from recurring, the surgeon may remove (strip) the vein.

Complications of Surgery
Potential side effects of these treatments include:
- Scarring.
- Skin burns.
- Infection.
- Injury to a nerve.
- Deep vein thrombosis (a blood clot in a vein deep inside your body).
Sclerotherapy can cause side effects that include:
- Redness or bruising for a few days where a needle went into your skin.
- Brown areas (for several months) on skin where the needle touched.
- Lumps or hardness for a few months.
Prevention
- Avoid standing for extended periods of time.
- Take frequent breaks to stretch and move about, especially if your profession demands you to be on your feet.
- Elevate your legs to increase blood flow to your heart by bringing your feet up above your waist.
- Keep your weight in check: Shedding extra pounds lowers the pressure inside your blood vessels.
- Stop using tobacco: Smoking harms blood arteries, reduces blood flow, and results in a host of health issues.
- Keep moving: Avoid sitting immobile for extended periods of time to enhance circulation.
- Attempt compression socks: Supportive clothing, such as support socks and pantyhose, can assist blood flow and compress your veins, which can slow the progression of varicose veins.
- Don’t forget to dress comfortably: Make sure your waistline is not too tight to promote blood flow.: The goal of this technique, also known as ligation and stripping, is to stop blood from pooling by tying off the afflicted vein.
- To stop varicose veins from recurring, the surgeon may remove (strip) the vein.

Complications if Not Treated
- Superficial thrombophlebitis: Blood clots can form inside varicose veins, causing a condition called superficial venous thrombosis or superficial thrombophlebitis. Thrombophlebitis is painful but isn’t usually dangerous. It’s also treatable.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): People with varicose veins have a higher risk of deep vein thrombosis, a blood clot in a vein deep inside your body.
- Pulmonary embolism: A blood clot in your body (usually resulting from DVT) can become lodged in your lung. Pulmonary embolism is a life-threatening condition that requires immediate treatment.
