Breast lumps
A breast lump is a mass that develops in your breast. While a breast lump can be a sign of breast cancer, often it is not related to cancer. Eight out of 10 breast lumps are noncancerous. If you feel a lump in your breast or under your arm, see your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider will figure out the cause of the breast lump and determine whether it needs additional workup or treatment.
Causes
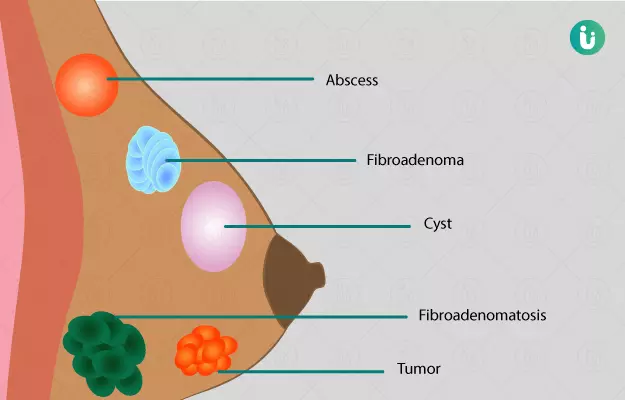
- Changes in the breast tissue (fibrocystic changes): Tiny, fluid-filled sacs and fibrous (rubbery) tissue feel like lumps.
- Breast cysts: Fluid-filled sacs form when fluid becomes trapped in the milk ducts. Cysts are common in premenopausal women.
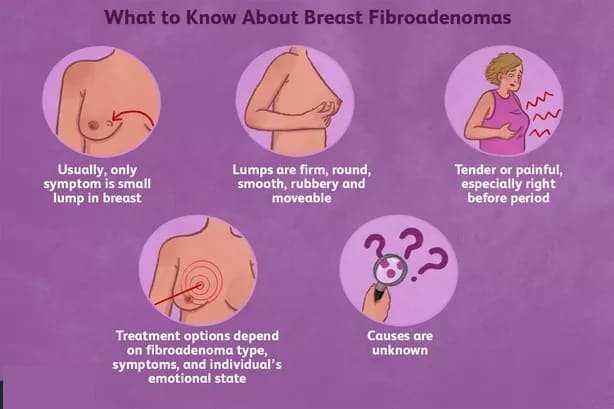
- Fibroadenomas: This benign (noncancerous) lump is the most common breast tumour in young women (20s and 30s). Fibroadenomas are most common during a person’s reproductive years.
- Breast infection: An infection in the breast tissue can cause a lump.
- Breast cancer: A tumour growing in the breast tissue causes a lump.
Tests And Treatment
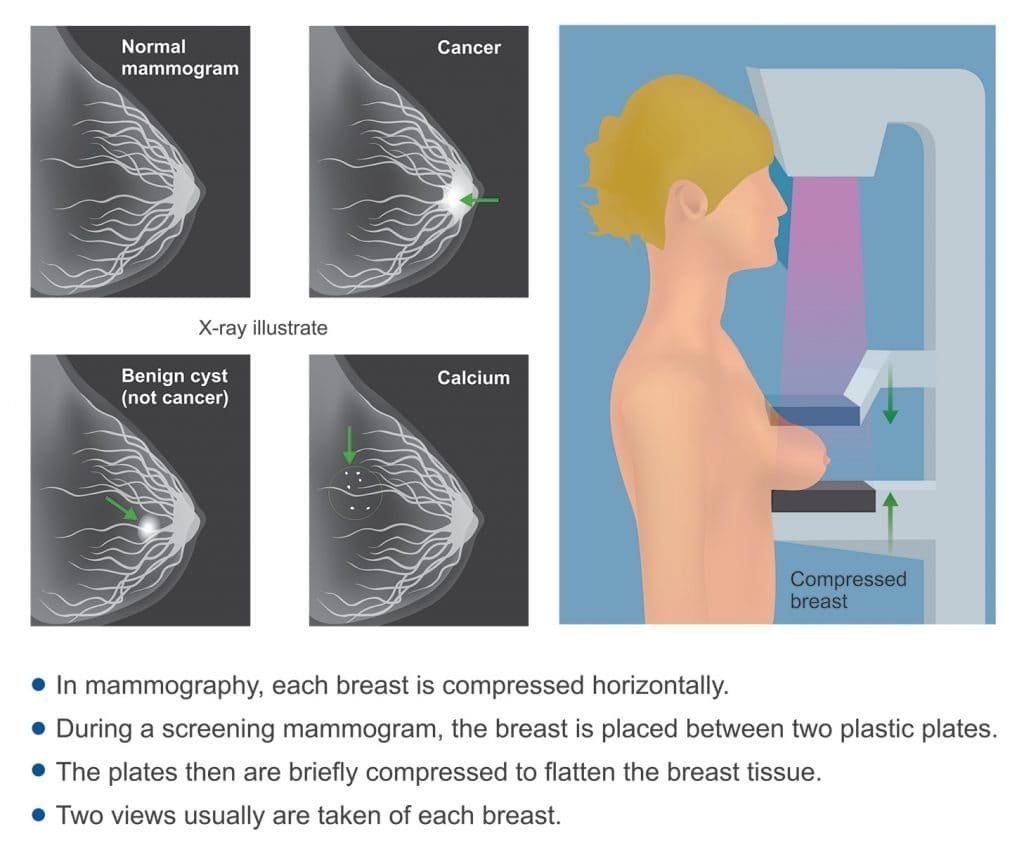
Breast MRI: This imaging scan uses magnetic fields to create detailed breast images.
Needle aspiration: Using a needle, your healthcare provider removes a sample of cells for evaluation.
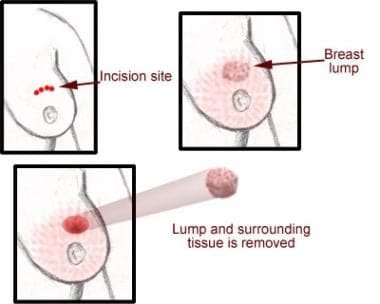
Biopsy: This procedure removes a larger tissue sample for analysis. There are several types of biopsy procedures. During a core biopsy, radiologists use a larger needle to remove a tissue sample. During an excisional biopsy, surgeons remove the entire breast lump.
Health history: Your healthcare provider asks you about your symptoms, medical history, and family history.
Breast exam (mammogram or ultrasound): These imaging scans provide detailed views of the breast.
Discussion about other tests you might need: Your healthcare provider may want to examine the lump further.
Management And Treatment
Sometimes, lumps disappear on their own. Younger people may get lumps related to the menstrual cycle (period). Those lumps go away by the end of the cycle. However, always notify your healthcare provider about any lumps. Your provider can figure out what is causing the lump and determine if it needs further workup or treatment.
Breast lump treatment includes:
- Antibiotics for a breast infection.
- Fluid drainage for a breast cyst (if it is large or painful).
- Excisional biopsy to remove a mass (if suspicious for cancer, painful or enlarging).
- Cancer treatment if the lump is biopsy-proven breast cancer. Cancer therapies may include lumpectomy, mastectomy, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy.
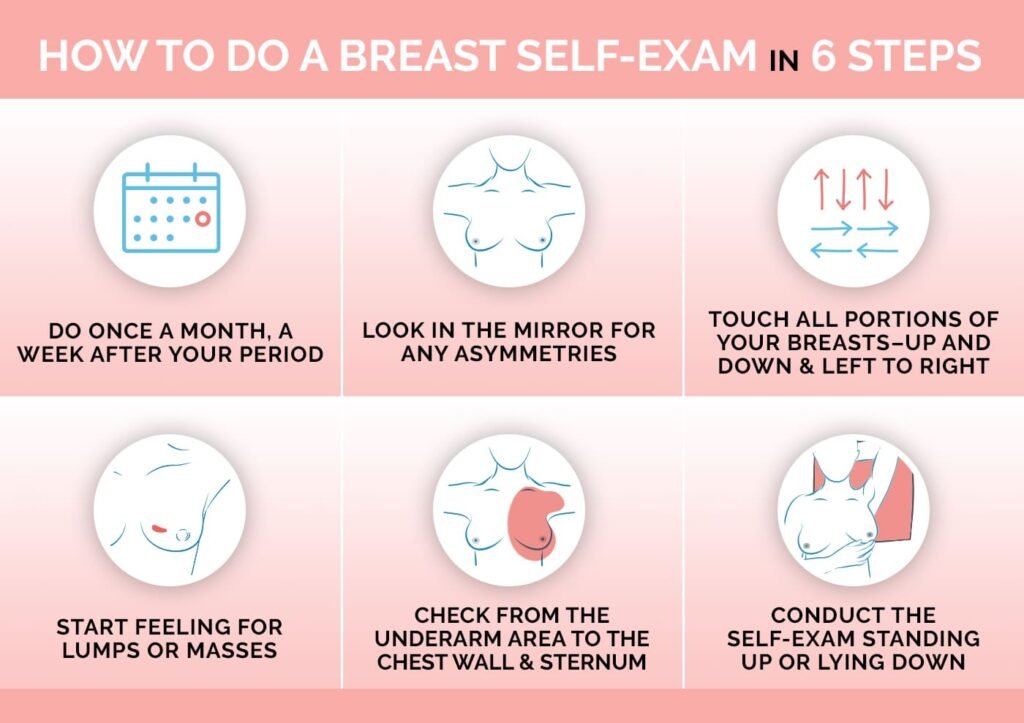
How can I maintain good breast health?
- Pay attention to your body. If you notice changes or something feels off, talk to your healthcare provider. Ways to keep your breasts healthy:
- Be aware of breast changes and report any concerns to your healthcare provider.
- Talk to your healthcare provider about screening options.
- Know your breast density and how it may affect your mammogram.
- Report changes in your family history to your provider every year.
When to call the Surgeon
- An unusual lump or mass in your breast or under your arm that feels harder than the rest of the breast or is different on one side as compared to the other.
- Other breast changes including nipple inversion (turning inward), dimpled skin, or bloody/clear nipple discharge.
- Redness, pain, or focal tenderness in your breast.
- Nipple changes such as excoriation or scaling. (Excoriation is an obsessive-compulsive mental disorder where you pick at your skin so much that you damage it.)
