Appendicitis
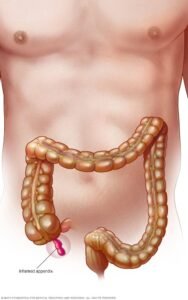
Appendix is a finger-sized tube located where the large and small intestines connect. It has no known function, but if it gets inflamed or infected (appendicitis), you will need immediate treatment.
An inflamed appendix may cause pain off and on. Or it may burst open (rupture), causing sudden, severe pain. A ruptured appendix can spread bacteria through the abdominal cavity. These bacteria trigger a serious, sometimes-fatal infection called peritonitis.
Appendicitis can occur at any age, although it is most common in people in their teens and 20s. Appendicitis in children most often occurs during the tween or teen years. But even elementary school-age children get appendicitis.
Laparoscopic Appendicectomy offers a modern, scar-minimizing approach for appendix removal. Dr. Durai Ravi ensures faster healing and minimal postoperative discomfort.
Causes
- It is not clear what brings on appendicitis. Something triggers an inflammation (irritation and swelling) or infection in your appendix.
- Abdominal injury or trauma.
- Blockage at the opening where the appendix connects to the intestines.
- Digestive tract infection.
- Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Growths inside the appendix.
Symptoms
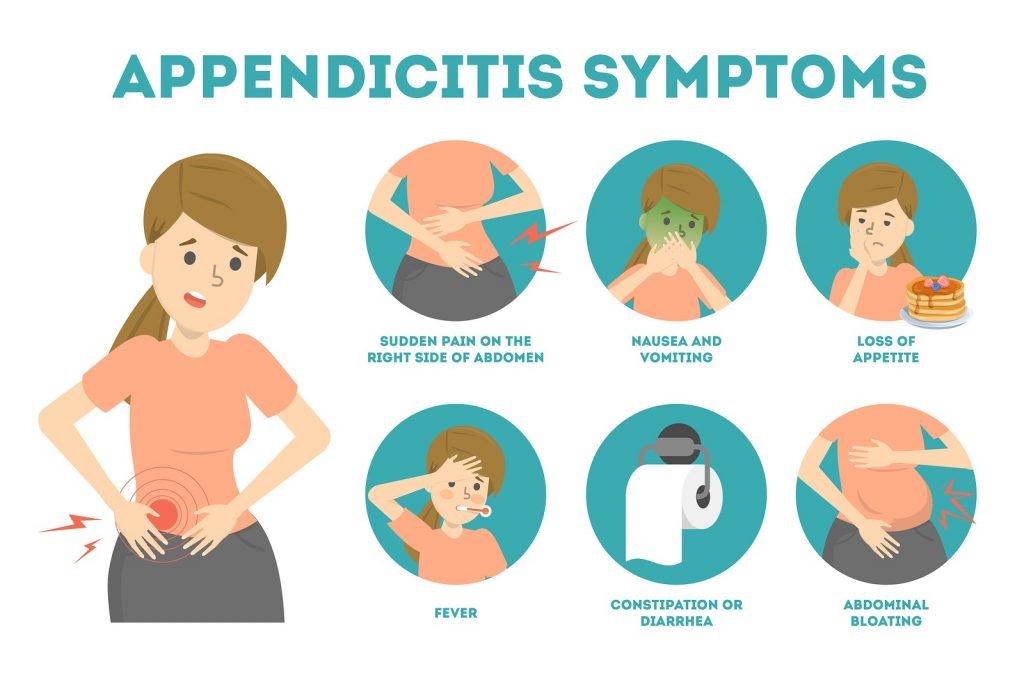
- Severe abdominal pain in the lower right belly — where your appendix is — is a key sign of appendicitis.
- Abdominal pain or tenderness that hurts more when you cough, sneeze, inhale or move.
- Swollen belly.
- Constipation.
- Diarrhoea.
- Inability to pass gas.
- Loss of appetite (not feeling hungry when you usually would).
- Low-grade fever (below 100 degrees F).
- Nausea and vomiting.
Diagnosis And Test
- physical exam.
- blood test.
- Computed tomography (CT) scans.
- An abdominal ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves to show images of organs.

Management And Treatment
- Most people with appendicitis need a surgery called an appendectomy. It removes a diseased appendix. If the appendix has not yet ruptured, surgery prevents that rupture and keeps infection from spreading.
- Before surgery, you receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics to treat infection. Some cases of mild appendicitis get better with antibiotics alone. Your Surgeon will watch you closely to determine if you need surgery. Surgery is the only way to treat abdominal infection when the appendix ruptures.
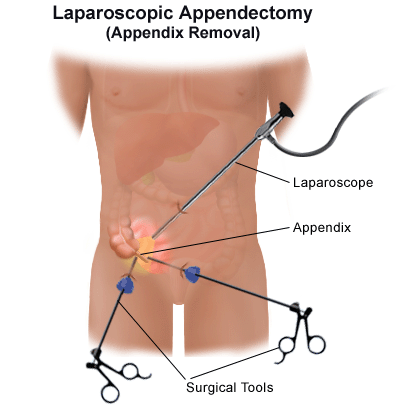
- If you need surgery, most appendectomies are done laparoscopically. Laparoscopic procedures take place with a scope through small incisions. This minimally invasive approach helps you heal faster, with less pain. You may need major abdominal surgery (laparotomy) if the appendix ruptures.
Complications of appendicitis
If it is not treated, a diseased appendix can rupture. A burst appendix can cause an infection that can lead to serious illness and even death. Complications include:
Abscess: You may develop an appendicular abscess, or a pocket of infectious pus. Your healthcare provider will place drainage tubes in your abdomen. These tubes remove fluid from the abscess before surgery. The drainage process may take a week or longer. During this time, you take antibiotics to fight infection. After the abscess is gone, you will have surgery to remove the appendix.
Abdominal infection: Peritonitis can be life-threatening if infection spreads throughout the abdomen. Abdominal surgery (laparotomy) removes the ruptured appendix and treats the infection.
Sepsis: Bacteria from a ruptured appendix can get into your bloodstream. If it does, it can cause a serious condition called sepsis. Sepsis causes widespread inflammation in many of your organs. It can be fatal. It requires hospital treatment with strong antibiotics.
Prevention
How can I prevent appendicitis?
There is no proven way to prevent appendicitis. Eating a high-fiber diet with lots of whole grains and fresh fruits and vegetables may help, although experts cannot explain why.
Outlook / Prognosis
What is the prognosis (outlook) for people with appendicitis?
Because the appendix has no known purpose, you should not notice any difference after having surgery to remove it. Some people who have laparoscopic surgery go home the same day or within 24 hours. Most people return to their usual active life within two to three weeks.
You will need more time in the hospital (if a week) to recuperate from open surgery. If your appendix ruptured, you may need long-term antibiotics to clear out the infection completely. Your recovery time may take six weeks or longer.
When should I call the Surgeon if treated conservatively or surgically?
If you had antibiotic-only treatment, call your healthcare provider if you notice signs of appendicitis again. You should also call your provider if you are recovering from appendectomy surgery, and you experience:
- Constipation
- Fever
- Infected surgical site (incision), with signs of redness, swelling or yellow pus
- Intense pain in your lower right abdomen
