Hemorrhoids
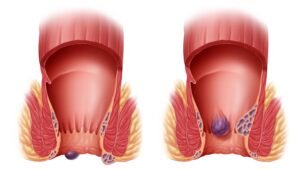
What are hemorrhoids (Piles)?
Hemorrhoids are swollen, enlarged veins that form inside and outside the anus and rectum. They can be painful, uncomfortable and cause rectal bleeding. hemorrhoids are also called piles.
How common are hemorrhoids?
They affect people of all ages, genders, races, and ethnicities. They are more common as you age, affecting more than half of people over age 50.
Who might get hemorrhoids?
Anyone can get symptomatic hemorrhoids, even teenagers.
What are the types of hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can happen inside or outside the rectum. The type depends on where the swollen vein develops.
External: Swollen veins form underneath the skin around the anus. External hemorrhoids can be itchy and painful. Occasionally, they bleed. Sometimes they fill with blood that can clot. This is not dangerous but can result in pain and swelling.
Internal: Swollen veins form inside the rectum. Your rectum is the part of the digestive system that connects the colon (large intestine) to the anus. Internal hemorrhoids may bleed, but they usually are not painful.
Prolapsed: Both internal and external hemorrhoids can prolapse, meaning they stretch and bulge outside of the anus. These hemorrhoids may bleed or cause pain.
What is the difference between hemorrhoids and anal fissures?
hemorrhoids and anal fissures cause similar symptoms, such as itching, pain and bleeding. While swollen veins cause hemorrhoids, a tear in the lining of the anus causes an anal fissure.
Blood in stools?
Blood in Stools should never be ignored. Dr. Durai Ravi provides accurate diagnosis and gentle treatment to address the underlying causes safely and effectively.
What causes hemorrhoids?
- Straining puts pressure on veins in the anus or rectum, causing hemorrhoids. You might think of them as varicose veins that affect your bottom.
- Any sort of straining that increases pressure on your belly or lower extremities can cause anal and rectal veins to become swollen and inflamed.
Hemorrhoids may develop due to:
- Pelvic pressure from weight gain, especially during pregnancy.
- Pushing hard to have a bowel movement (poop) because of constipation.
- Straining to lift heavy objects or weightlifting.
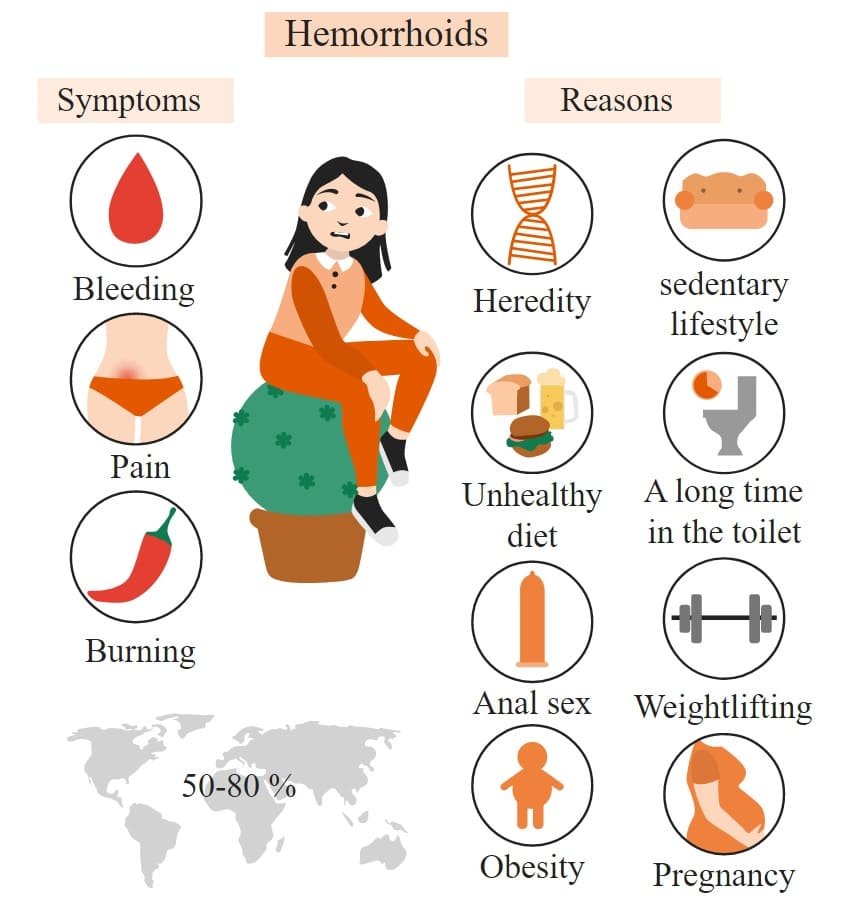

What are the symptoms of hemorrhoids?
- Internal haemorrhoids rarely cause pain (and typically cannot be felt) unless they prolapse. Many people with internal haemorrhoids do not know they have them because they do not have symptoms.
- If you have symptoms of internal haemorrhoids, you might see blood on toilet paper, in stool or the toilet bowl. These are signs of rectal bleeding.
Signs of external hemorrhoids include:
- Itchy anus.
- Hard lumps near the anus that feel sore or tender.
- Pain or ache in the anus, especially when you sit.
- Rectal bleeding.
- Prolapsed haemorrhoids can be painful and uncomfortable. You may be able to feel them bulging outside the anus and gently push them back inside.
What other conditions cause hemorrhoid-type symptoms?
Different gastrointestinal disorders can cause rectal bleeding and other symptoms like hemorrhoids. Some of these disorders are life-threatening.
Bowel diseases that can cause bleeding include:
Colon cancer.
Crohn’s disease.
Ulcerative colitis.
DIAGNOSIS:
Your healthcare provider diagnoses hemorrhoids based on symptoms and a physical exam. You may also have:
Digital rectal exam: Your provider inserts a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to feel for swollen veins.
Proctoscopy: Your provider uses a proctoscopy to view the lining of the anus and rectum.
Sigmoidoscopy: Your provider uses a sigmoidoscopy (lighted tube with a camera) to view inside the lower (sigmoid) part of the colon and rectum. Procedure types include flexible sigmoidoscopy and rigid sigmoidoscopy.
These tests may be uncomfortable but are not painful. They typically take place in a Surgeon’s office or outpatient centre without anaesthesia. You go home the same day.
Your provider may perform a colonoscopy to confirm findings from other tests or check for signs of colon cancer. This outpatient procedure requires anaesthesia.
Management And Treatment
What are the complications of hemorrhoids?
Hemorrhoids can be uncomfortable and painful, but they do not tend to cause serious problems. Rarely, people with hemorrhoids develop:
- Anaemia.
- Blood clots in external haemorrhoids.
- Infection.
- Skin tags (flap of tissue that hangs off skin).
- Strangulated haemorrhoids (muscles in the anus cut off blood flow to a prolapsed internal haemorrhoid).
How can I treat haemorrhoids at home?
Hemorrhoids often go away on their own without treatment. Symptoms like pain and bleeding may last one week or slightly longer. In the meantime, you can take these steps to ease symptoms:
- Apply over-the-counter medications containing lidocaine, witch hazel or hydrocortisone to the affected area.
- Drink more water.
- Increase fiber intake through diet and supplements. Try to obtain at least 20-35 grams of daily fiber intake.
- Soak in a warm bath (sitz bath) for 10 to 20 minutes a day.
- Soften stool by taking laxatives.
- Take nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for pain and inflammation.
- Use toilet paper with lotion or flushable wet wipes to gently pat and clean your bottom after pooping. You can also use a tissue or washcloth moistened with water. (Discard wipes in the trash, not by flushing. Launder washcloths separately in hot water to avoid spreading infections often found in poop.)
How do healthcare providers treat hemorrhoids?
You should see your healthcare provider if symptoms get worse or interfere with your daily life or sleep. Also seek help if signs do not improve after a week of at-home treatments.
Non-invasive management:
Rubber band ligation: A small rubber band placed around the base of a hemorrhoid cuts off blood supply to the vein.
Electrocoagulation: An electric current stops blood flow to a hemorrhoid.
Infrared coagulation: A small probe inserted into the rectum transmits heat to get rid of the hemorrhoid.
Sclerotherapy: A chemical injected into the swollen vein destroys hemorrhoid tissue.
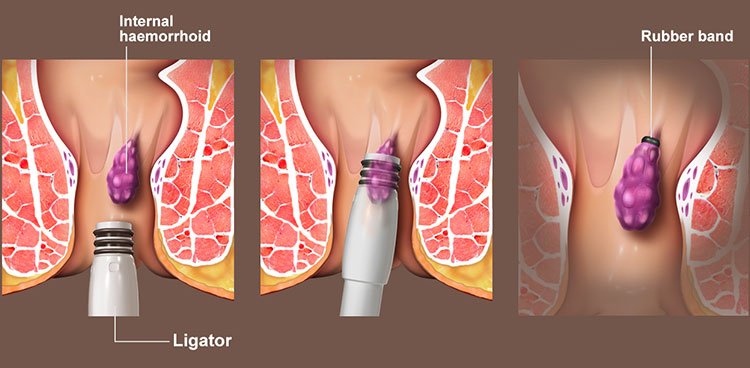
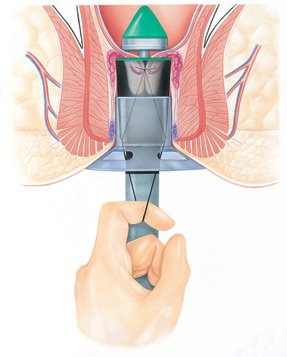
Surgical treatments include:
Hemorrhoidectomy: Surgery removes large external hemorrhoids or prolapsed internal ones.
Hemorrhoid stapling: A stapling instrument removes an internal hemorrhoid. Or it pulls a prolapsed internal hemorrhoid back inside the anus and holds it there.
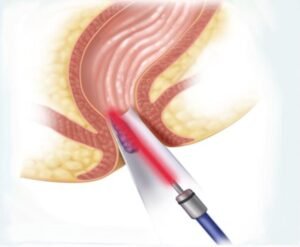
Laser Hemorrhoidopexy: Your surgeon uses a laser to coagulate the hemorrhoidal veins there by reducing the size and symptoms. It can be done for Grade 1 to Grade 3 hemorrhoids.

Prevention
- Do not sit too long or push too hard on the toilet.
- Go the toilet when the urge hits — do not delay bowel movements.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Eat more high-fiber foods (fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains) or take supplements. Women should aim for 25 grams of fiber per day, while men should get 35 grams of fiber.
- Stay physically active. Being on the move keeps bowels moving.
- Take laxatives or use enemas only as recommended by your healthcare provider. Too many laxatives or enemas can make it hard for your body to regulate how you poop.
OUTLOOK / PROGNOSIS
- Most hemorrhoid symptoms improve within a week with at-home treatments. If hemorrhoids cause extreme pain and discomfort, a medical procedure or even surgery may help.
When should I call the Surgeon?
- Abdominal pain.
- Chronic constipation or diarrhoea.
- Fever and chills.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Severe rectal bleeding and pain.
